SWOT Analysis
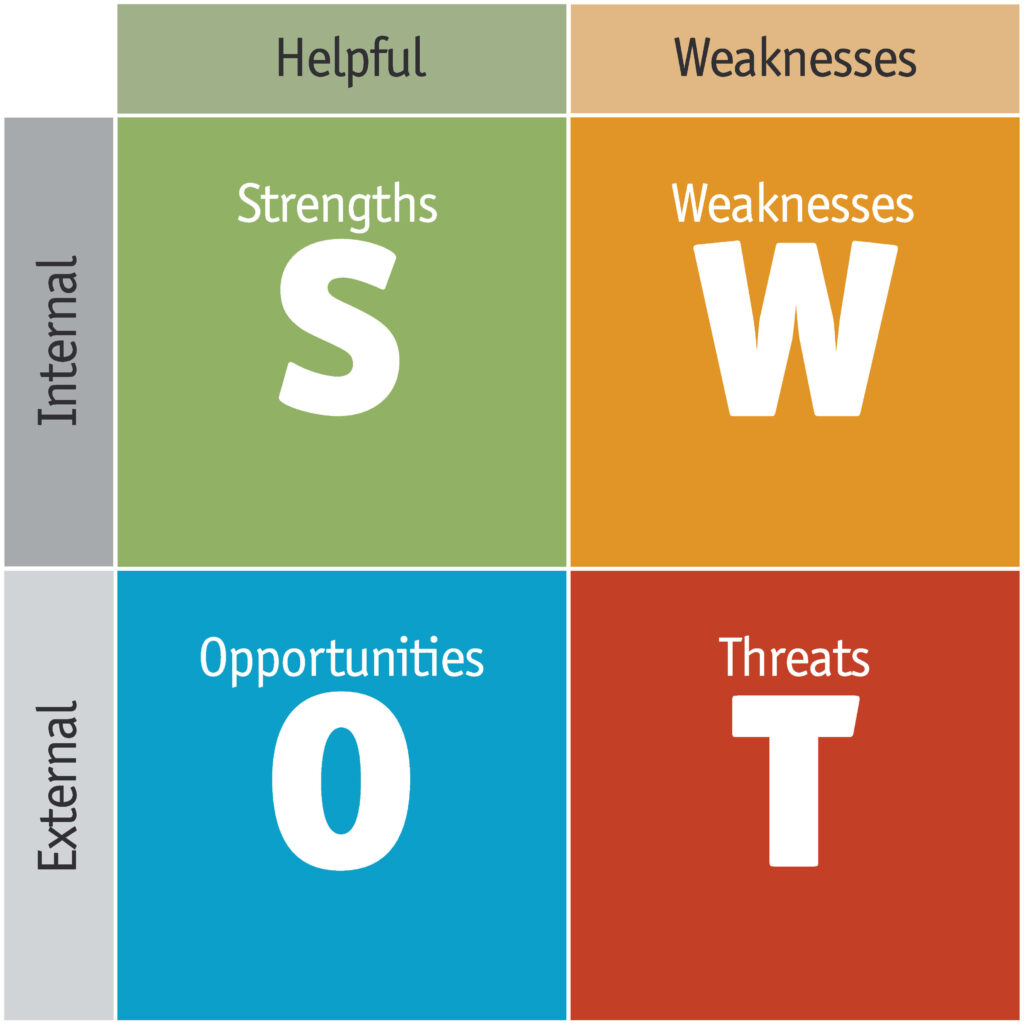
SWOT is a simple and widely used tool for strategic planning and stands for: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
The purpose of SWOT analysis is to identify and list all the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of a company or business.
The benefit of SWOT Analysis is to provide a list of valuable information, allowing the team to organize action plans in order to reduce risks and seize opportunities.
Risk factor is any event that can affect, in whole or in part, the chances of a project’s success, and risk is the probability that this risk factor will actually occur.
The strengths and weaknesses are internal factors, which are within the company itself. Opportunities and threats have an external origin.
The internal environment is usually defined as the one over which the company has control and can act on it.
A patent, for example, is not within the company, but the company has control over it. Therefore, all factors on which it is possible to intervene are part of the internal environment, such as its personnel, machinery, sales policies, used technologies, management software and systems, vehicle fleets, branch network, customer portfolios, organizational culture, investment capacity, etc.
Strengths
These are elements and characteristics of your internal environment that represent an advantage over your competition.
For example, a hotel that has an excellent ocean front location and easy access might consider this as strengths. As well, a hospital that has an extremely qualified medical staff or a prestigious clothing brand desired by the public.
Some examples of strengths are:
- Product with superior quality;
- Best price product;
- Service appreciated by customers;
- United, motivated and highly productive team;
- Important assets such as machinery and real estate;
- Good location;
- Good suppliers;
- Good processes.
Weaknesses
Analogous to strengths, weaknesses are characteristics and elements of the internal environment that disadvantage the organization and the project in relation to the competition.
Imagine a food factory that is located far from major distribution centers and therefore has high transport costs, or an airline that has an old aircraft fleet and therefore has more maintenance costs and problems with delays in its flights.
Note that in these two examples the company has control over these weaknesses and can try to change it in some way, even if it is something very expensive and complex, as in these two cases.
Some examples of weaknesses:
- Poorly trained or unmotivated staff;
- Lack of organization and documentation of processes;
- Management systems do not meet the needs of the industry;
- Lack of standardization in the production process;
- Lack of quality control in the production process;
- Losses in the production process;
- Lack of organization and control in the stock.
Questions to discover strengths and weaknesses:
- How can team quality be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our competence in management and the leader’s quality be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our infrastructure be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our technology be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our location be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our brand be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our capital structure be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our supply chain be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
- How can our distribution chain be a competitive advantage (or disadvantage)?
The external environment has factors over which the company has no control, such as the weather, interest rates, changes in legislation, exchange rates, natural disasters, environmental policies, wars, economic crises, elections, etc.
Opportunities
Whenever an external factor creates a favorable scenario for the company, it represents an opportunity.
The World Cup is a good example of an opportunity for hotels, restaurants and airlines during the period of the games.
Some examples of opportunities:
- Development of new products and services;
- Expansion of the portfolio of clients and sectors of the economy;
- Government incentives for your industry;
- Government incentives for its customer sectors;
- Changes in tax planning;
- New technologies available;
- Reduction of international trade barriers;
- Economy growth;
- Foreign investments;
- Expansion of your potential customers’ credit.
Threats
Threats represent all the elements or scenarios that create an unfavorable environment for the company and project, and over which the company has no control.
In the case of a hotel, a season of heavy storms and bad weather are threats, just as rising fuel prices and the dollar are threats for the airline.
Some examples of threats:
- New and bigger competitors;
- Loss of key employees;
- Change of laws and taxes;
- Product counterfeiting;
- Impacting currency changes;
- Changes in import and export regulations;
- Economic downturn;
- Disruptive innovations in your business segment;
- End of government incentives.
Questions to discover Opportunities and Threats:
Questions about opportunities and threats are typically related to six main areas: political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal.
The main questions can be:
- What political factors could be a threat to my business?
- What economic factors could be a threat to my business?
- What social factors could be a threat to my business?
- What technological factors could be a threat to my business?
- What environmental factors could be a threat to my business?
- What legal factors could be a threat to my business?

Performing the SWOT analysis is not the end of the process. After filling the data, the next step is to identify priorities and define an action plan, in order to mitigate the weaknesses, reduce the risk of threats and take advantage of strengths and opportunities.It is important to assign responsibilities and define deadlines in the action plan, aiming to periodically monitor the actions evolution and achieved results.
Written by Prof. Fabio Guedes